What Is Meant By The Term "Dividend Yield"?
Dec 17, 2023 By Triston Martin
What is a Dividend Yield? The dividend yield is an important financial metric for investors because it indicates how much income they may anticipate receiving from a stock investment. It evaluates the stock price in relation to the dividends paid out by a firm. Dividends are payments made by companies to their shareholders as a share of their profits. They are part of a company's earnings given to its owners. Divide the annual dividend per share by the stock price per share. This will provide you with the dividend yield. For example, if a company pays a yearly dividend of $2 per share and its stock is worth $40, its dividend yield would be 5%. This means that if an investor bought the stock at $40 per share, dividends alone would give them a 5% return on their investment.
What Is Dividend Yield?
The dividend yield is the percentage of a share of a stock's current market price that is paid out in dividends to shareholders over a year. It is found by dividing the annual premium paid per share by the current price on the stock market. For example, if a company pays a dividend of $2 per share per year and its stock trades at $50 per share, the dividend yield is 4% ($2 divided by $50).
Why Is Dividend Yield Important?
The dividend yield is an essential metric for investors because it provides insight into a company's financial health and performance. If a company's dividend yield is high, it may be an indication that it is successful and has extra cash flow that it may provide to shareholders in the form of dividends. On the other hand, a low dividend yield may indicate that a company is reinvesting its profits in the business or has limited cash flow.
How Is Dividend Yield Calculated?
Divide the dividend paid out per share each year by the stock's price per share to get the dividend yield. Dividend yield is calculated as follows:
Dividend Yield = Dividends Paid In A Year / Current Stock Price
If a corporation has a stock price of $40 per share and distributes $2 per share year in dividends, the dividend yield is 5%.
Types Of Dividend Yield
There are two types of dividend yield: forward dividend yield and trailing dividend yield.
Forward Dividend Yield
Forward dividend yield calculates the expected dividend yield for the following year. It is calculated using the current stock price and the estimated dividend payout for the next year. This calculation assumes that the company will maintain the same dividend payout.
Trailing Dividend Yield
Trailing dividend yield is a dividend yield calculation based on the dividends paid over the past year. It is calculated using the actual dividends paid over the past year and the current stock price. This calculation reflects the real dividends paid by the company over the past year.
Advantages Of Dividend Yield

Dividend yield offers several advantages to investors:
Predictable Income
Dividends provide investors with a predictable stream of income. Investors can rely on regular dividend payments to supplement their income, which helps reduce the overall risk of their investment portfolio.
Potential for Capital Appreciation
Paying dividends is a mature, stable company with a history of generating steady profits. These companies may also have a strong track record of increasing dividend payments. As a result, investing in dividend-paying companies can potentially provide investors with both regular income and the potential for capital appreciation.
Indication of Financial Health
If you want to know how well a firm is doing financially, look no further than its dividend yield. It has been hypothesized that a low dividend indicates a firm is reinvesting its profits in order to expand, whereas a good dividend yield is indicative of financial stability and profitability.
Disadvantages Of Dividend Yield
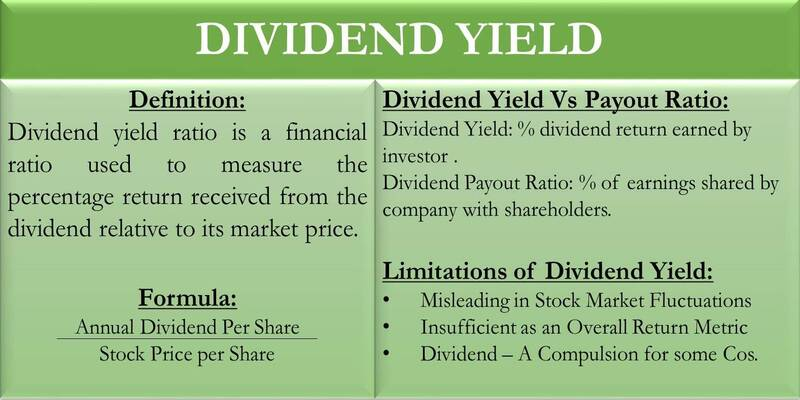
Dividend yield also has some disadvantages:
Limited Growth Potential
Dividend-paying companies are mature, established companies that may have limited growth potential. As a result, investing in dividend-paying companies may offer a different potential for capital appreciation than investing in growth-oriented companies.
Risk of Dividend Reduction
Companies that pay dividends are not obligated to maintain the same dividend payout in the future. If a company's profits decline
Or it faces other financial challenges and may reduce its dividend payout or suspend it altogether. This can negatively impact the value of an investor's portfolio and lead to a decrease in income.
Conclusion
The dividend yield is a valuable metric for investors looking for a steady income and potential capital appreciation. It provides insight into a company's financial health and can be used for stock selection, portfolio management, and evaluation of dividend policies. However, investors should be aware of the risks associated with investing in dividend-paying stocks, such as limited growth potential and the risk of dividend reductions. It is essential to conduct thorough research and analysis before making investment decisions based on dividend yield.








